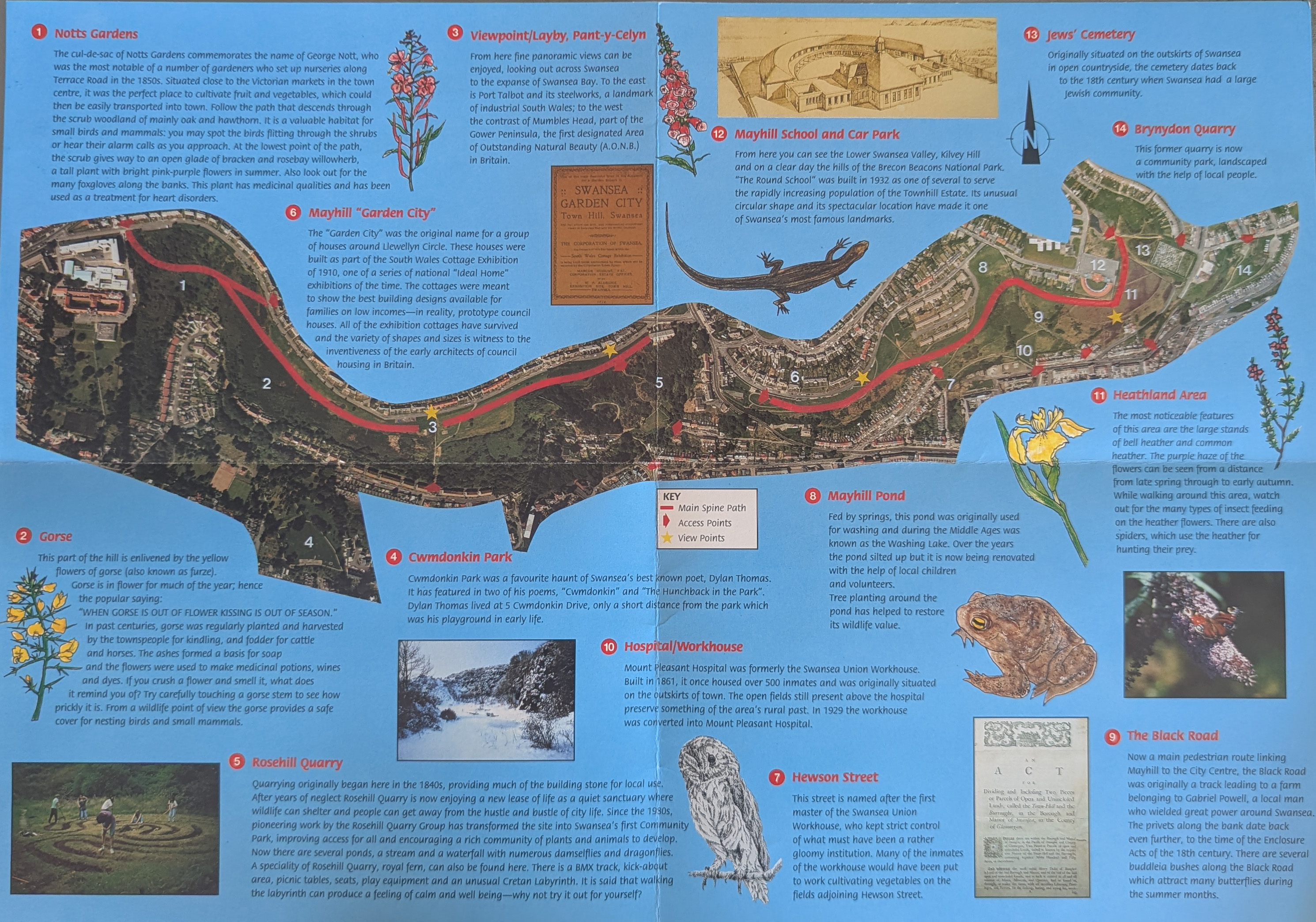
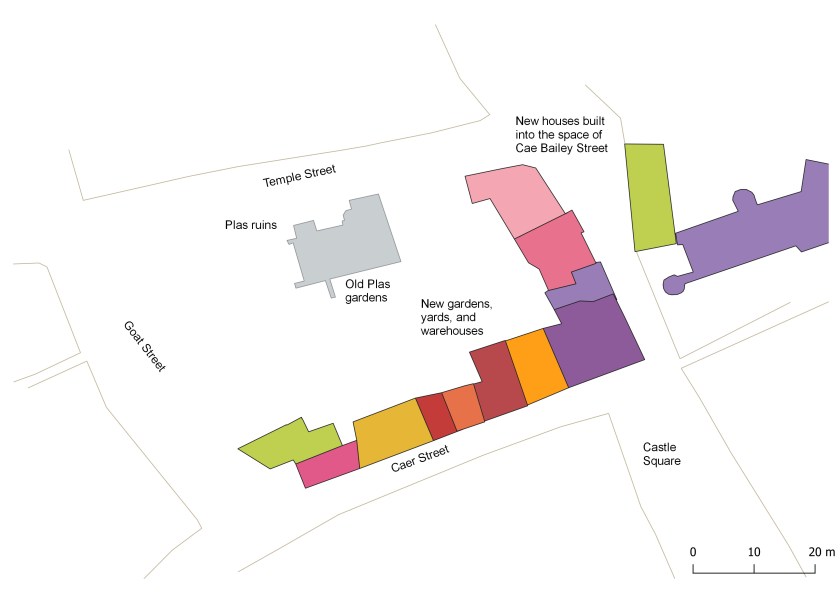
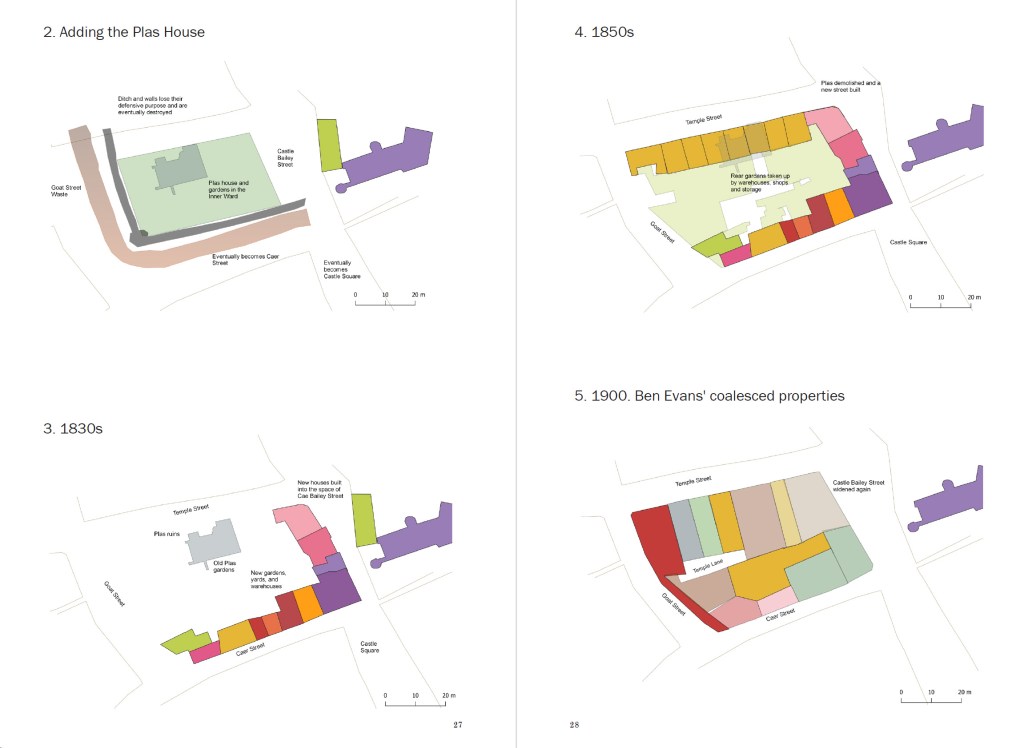
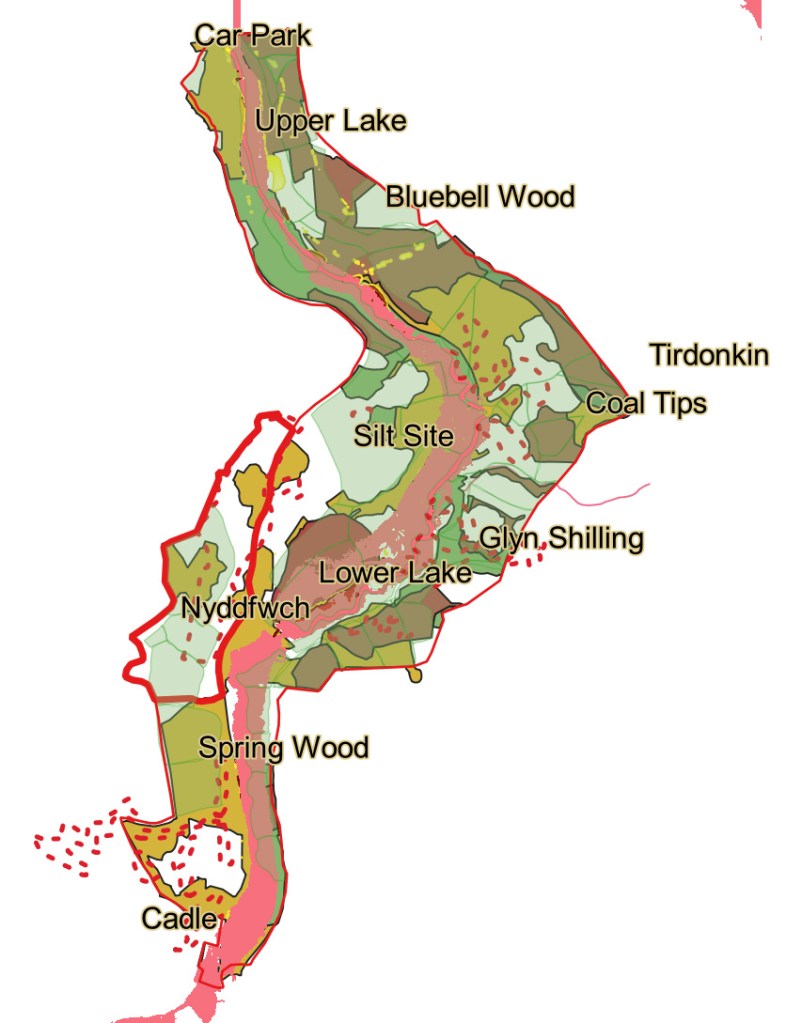
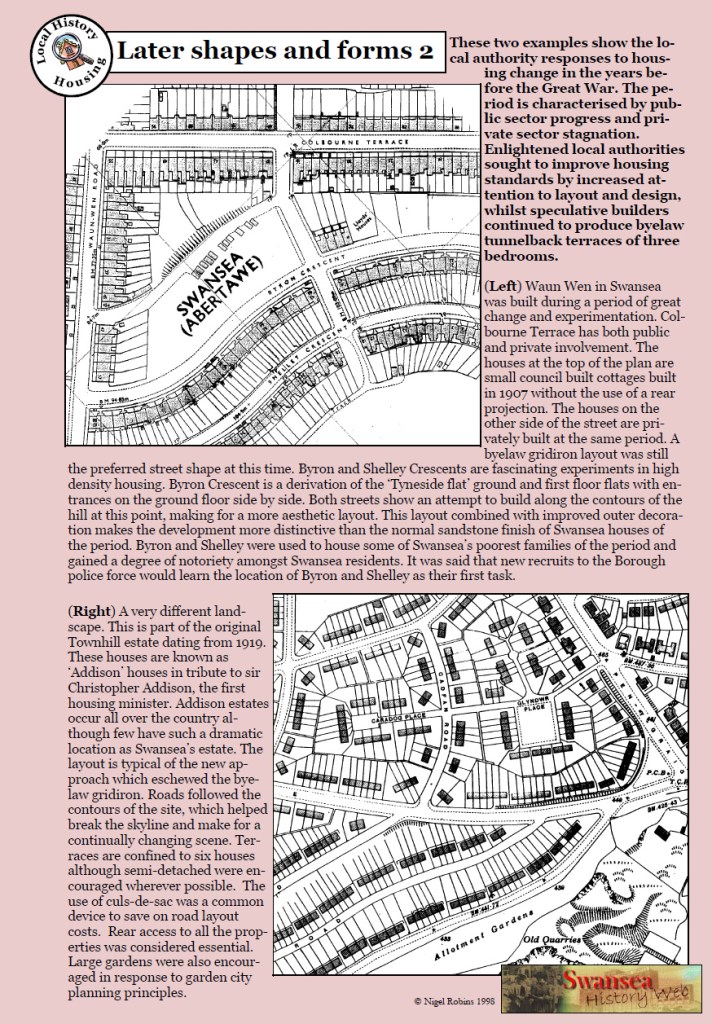
It was good to see the Fortieth Anniversary of the Rosehill Quarry park this afternoon. I remember it being set up as the place was a biodiversity hotspot on the hill long before it was transformed by the Rosehill Quarry Group. I can remember it wasn’t a completely popular thing to do in the early 1980s, as increasing access to an area known for trouble was not universally welcomed. Four decades later, it looks like it was always there.
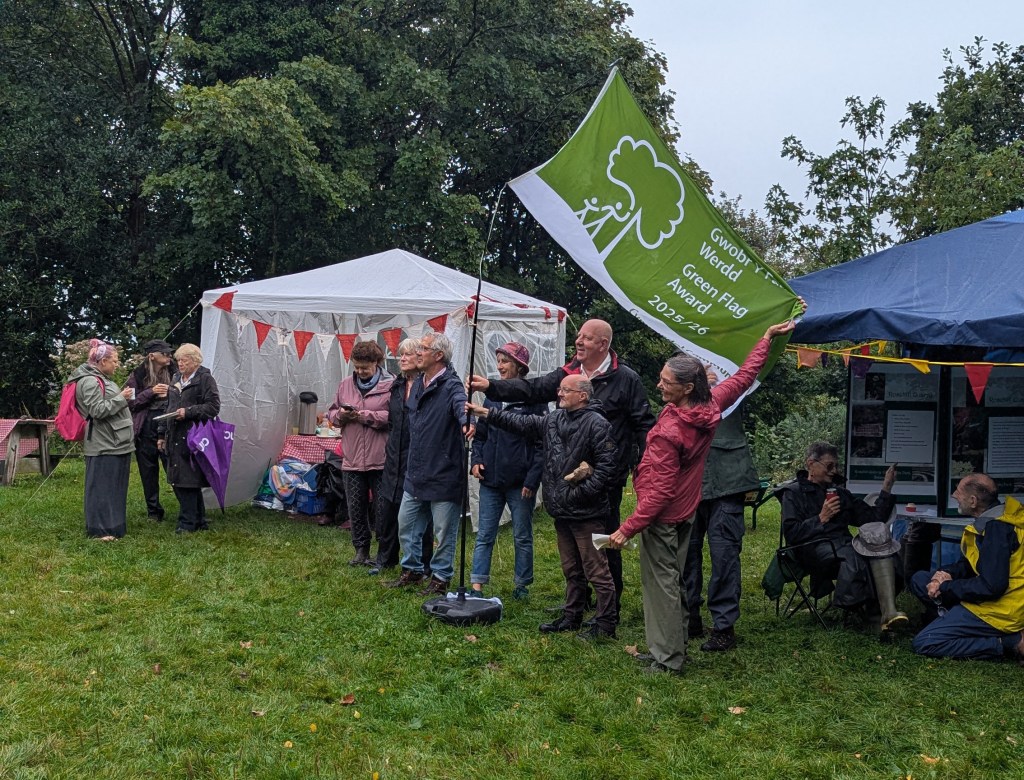

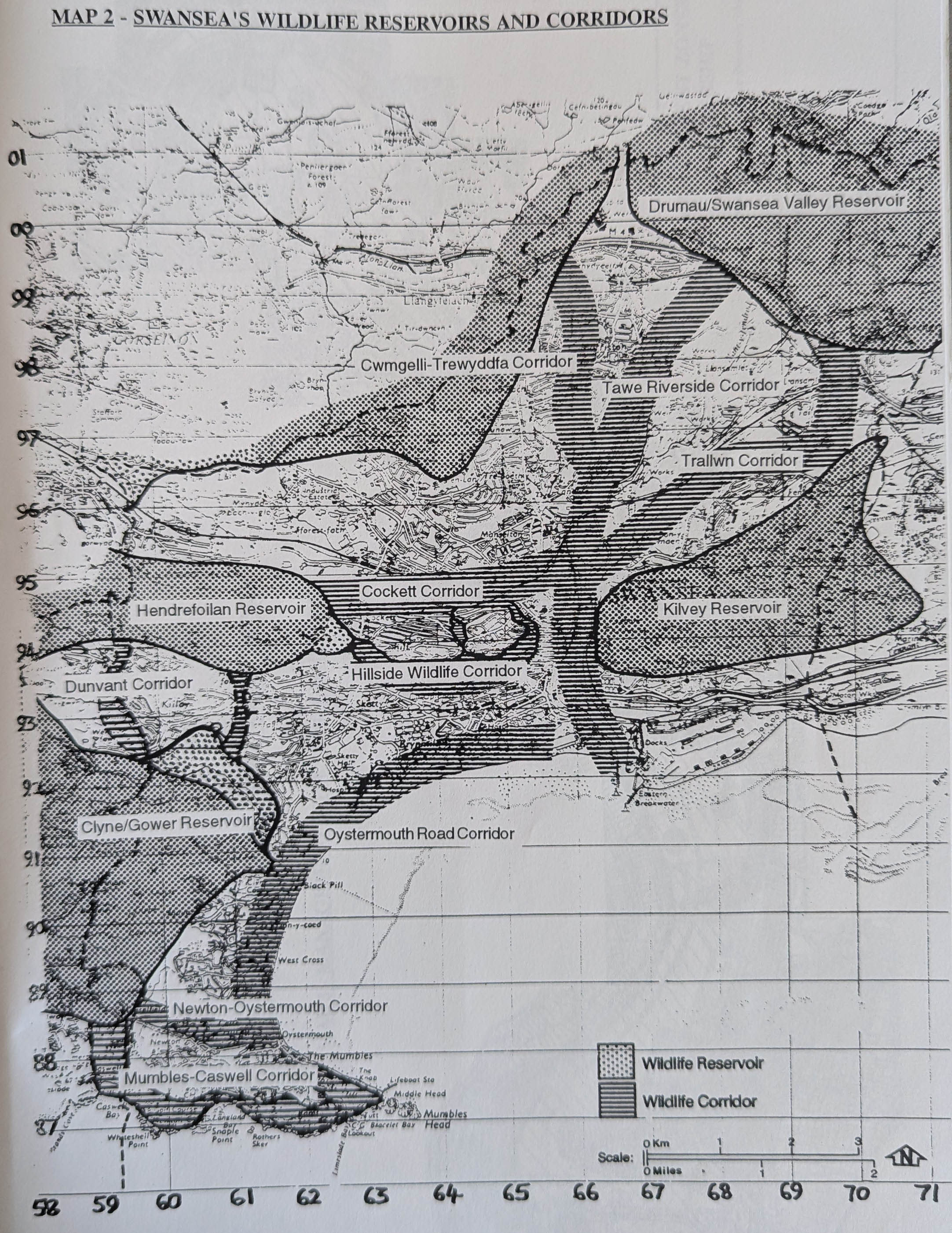
I remember writing the notes for a publicity pamphlet some years later when the City Council rebranded the area as the ‘Hillside Wildlife Corridor’ as part of the 1990 landmark Strategy for Greening the City. In those days, Swansea was zoned into a series of wildlife corridors and wildlife reservoirs. With bitter irony for what is about to happen, Kilvey was recognised as a wildlife reservoir.
It was particularly good to see Councillor D. H Hopkins say a few words about Rosehill, as he was central to the setting up of the Wildlife Corridor in the 1990s. He was far too modest about his role, and for me at least, he brought a welcome sense of continuity as if to confirm the long commitment to creating and maintaining the green space. For my part, I often gave little history talks about the area to the Group in the early days, always tempted by the fabulous cakes that Margaret Burdett would bring to the meetings.
I think it is also the tenth year the site has been awarded a Green Flag. On Kilvey, we had our first Green Flag this year.
Rosehill has always had unfailing political support from the Council (both City and its successor County Council). The area has transformed into a green jewel for plants and wildlife, and both the Council and the new crop of volunteers have done a fantastic job. One day, I hope Kilvey will get such good political support.
Among about thirty people there, I only recognised one face. A new generation of people has taken over, which made me feel rather old.